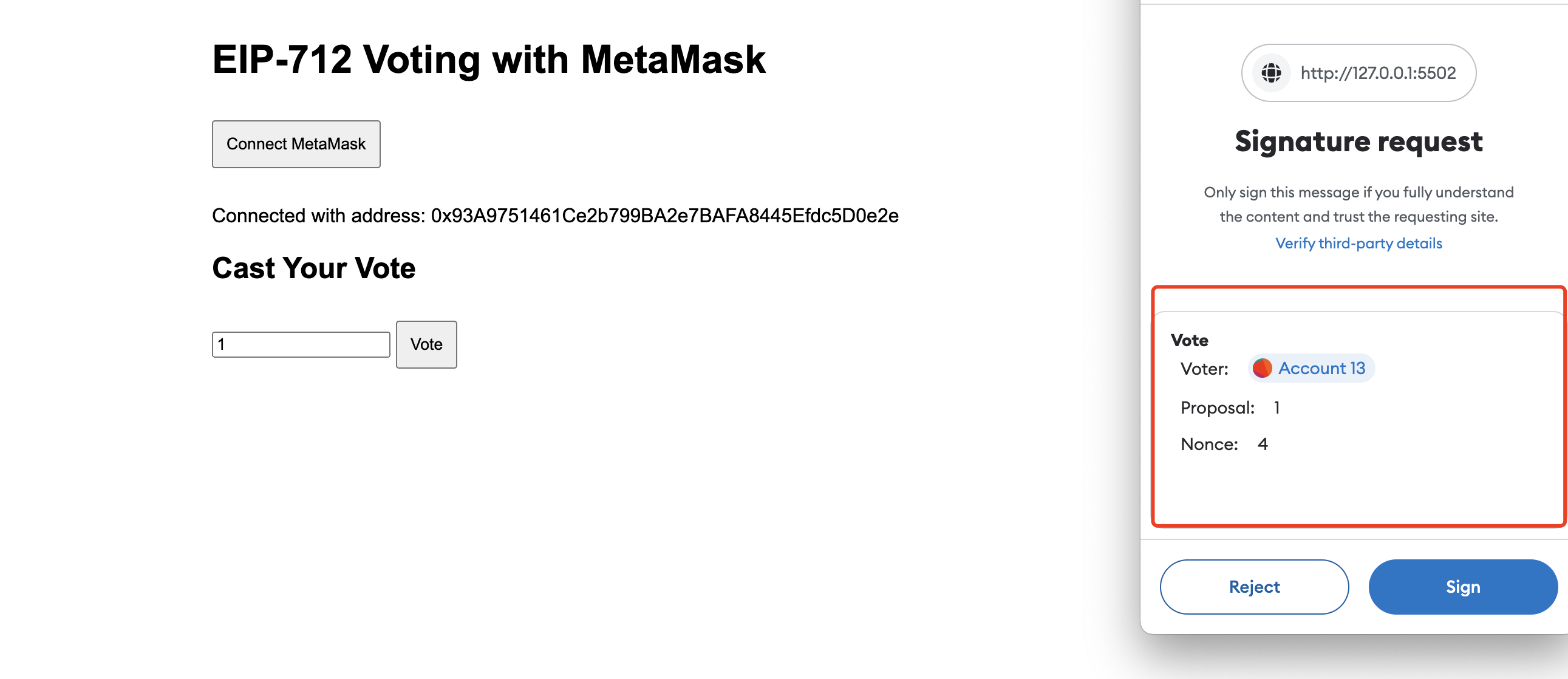
如何使用 EIP-712 签名
介绍EIP-712
EIP-712,即“带有类型结构化数据的哈希与签名”,是以太坊改进提案中的一个标准。 它提供了一种标准化的方法来签署结构化数据,使得签名过程更安全且用户友好。
EIP-712 签名的关键组成部分
-
EIP712域: 每个 EIP-712 签名都必须包含一个 EIP712域部分。 该部分包含有关合约和环境的重要信息。
EIP712Domain: [
{ name: "name", type: "string" },
{ name: "version", type: "string" },
{ name: "chainId", type: "uint256" },
{ name: "verifyingContract", type: "address" },
];这些信息会在签名过程中显示,并确保签名只能通过特定链上的特定合约进行验证。
-
域对象: 在你的签名脚本中,需要提供域信息:
const domain = {
name: "EIP712Voting",
version: "1",
chainId: 71, // Conflux eSpace testnet
verifyingContract: "0xDD1184EeC78eD419d948887B8793E64a62f13895",
}; -
自定义类型: 你需要定义与合约结构相匹配的自定义类型:
const types = {
Vote: [
{ name: "voter", type: "address" },
{ name: "proposal", type: "uint256" },
{ name: "nonce", type: "uint256" },
],
}; -
消息: 创建一个包含要签名数据的消息对象:
const value = {
voter: await signer.getAddress(),
proposal: 1, // Voting for proposal 1
nonce: await contract.nonces(signer.address),
}; -
签名过程: 使用钱包的
signTypedData()方法来创建签名:const signature = await signer.signTypedData(domain, types, value);
EIP-712的优点
- 提高可读性: 用户可以清楚地看到他们在签署什么,减少了恶意交易的风险
- 增强安全性:结构化格式有助于防止某些类型的钓鱼攻击。
- 更好的用户体验: 钱包和 dApp 可以显示更有意义的签名请求。
- 跨平台一致性:确保在不同的以太坊兼容平台上行为一致。
在本教程中,我们将使用 Hardhat 在 Conflux eSpace 网络上实现 EIP-712 签名,并创建一个简单的投票系统来演示其用法。 我们的投票系统将允许用户在链下签署他们的投票并将其提交到区块链,从而确保隐私和效率。
1. 项目设置
首先,确保你已经安装了 Node.js 和 npm。 然后,创建一个新的项目目录并进行初始化:
mkdir eip712-conflux-demo
cd eip712-conflux-demo
npm init -y
Install the necessary dependencies:
npm install --save-dev hardhat @nomicfoundation/hardhat-toolbox @openzeppelin/contracts dotenv
2. 配置Hardhat
创建Hardhat配置文件hardhat.config.js:
require("@nomicfoundation/hardhat-toolbox");
require("dotenv").config();
module.exports = {
solidity: "0.8.24",
networks: {
eSpaceTestnet: {
url: "https://evmtestnet.confluxrpc.com",
accounts: [process.env.PRIVATE_KEY],
},
},
};
创建一个.env文件存储你的私钥:
PRIVATE_KEY=your_private_key_here
确保将.env添加到你的.gitignore文件中。
3. 编写智能合约
创建一个contracts/EIP712Voting.sol文件:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/utils/cryptography/ECDSA.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/utils/cryptography/EIP712.sol";
contract EIP712Voting is EIP712 {
using ECDSA for bytes32;
mapping(uint256 => uint256) public voteCount;
// TypeHash for the Vote struct used in EIP-712 signing
bytes32 private constant VOTE_TYPEHASH =
keccak256("Vote(address voter,uint256 proposal,uint256 nonce)");
mapping(address => uint256) public nonces;
event VoteCast(address indexed voter, uint256 indexed proposal);
constructor() EIP712("EIP712Voting", "1") {}
function castVote(uint256 proposal, bytes memory signature) external {
// Generate the hash of the structured data
bytes32 structHash = keccak256(
abi.encode(
VOTE_TYPEHASH, // Type hash of the Vote struct, ensures data structure consistency
msg.sender, // Address of the voter
proposal, // ID of the proposal being voted on
nonces[msg.sender] // Current nonce of the voter, prevents replay attacks
)
);
// structHash now contains a unique identifier of the vote data
// Generate the final hash using the EIP-712 standard's _hashTypedDataV4 function
bytes32 hash = _hashTypedDataV4(structHash);
// hash is now the final hash combining the structured data hash and the domain separator
// This final hash is used to verify the EIP-712 signature
// The domain separator includes contract name, version, chain ID, and contract address,
// ensuring the signature is only valid for this specific contract and network
address signer = ECDSA.recover(hash, signature);
require(signer == msg.sender, "EIP712Voting: Invalid signature");
voteCount[proposal]++;
nonces[signer]++;
emit VoteCast(signer, proposal);
}
function getVoteCount(uint256 proposal) external view returns (uint256) {
return voteCount[proposal];
}
}
该合约实现了EIP-712签名验证和投票功能。
4. 编写部署脚本
创建一个scripts/deploy.js文件:
const hre = require("hardhat");
async function main() {
const EIP712Storage = await hre.ethers.getContractFactory("EIP712Voting");
const eip712Storage = await EIP712Storage.deploy();
// Wait for the contract to be deployed
await eip712Storage.waitForDeployment();
// Get the deployed contract address
const address = await eip712Storage.getAddress();
console.log("EIP712Storage deployed to:", address);
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exitCode = 1;
});
5. 部署合约
运行以下命令来部署合约:
npx hardhat run scripts/deploy.js --network eSpaceTestnet
记下输出的合约地址。
6. 创建签名脚本
创建一个scripts/sign.js文件:
const hre = require("hardhat");
require("dotenv").config();
async function main() {
const [signer] = await hre.ethers.getSigners();
const contractAddress = "<YOUR_DEPLOYED_CONTRACT_ADDRESS>";
const domain = {
name: "EIP712Voting",
version: "1",
chainId: 71, // Conflux eSpace testnet
verifyingContract: contractAddress,
};
const types = {
Vote: [
{ name: "voter", type: "address" },
{ name: "proposal", type: "uint256" },
{ name: "nonce", type: "uint256" },
],
};
const EIP712Voting = await hre.ethers.getContractFactory("EIP712Voting");
const contract = EIP712Voting.attach(contractAddress);
const nonce = await contract.nonces(signer.address);
const value = {
voter: await signer.getAddress(),
proposal: 1, // Assume we're voting for proposal 1
nonce: nonce,
};
// Use the new signTypedData method
const signature = await signer.signTypedData(domain, types, value);
console.log("Signer:", await signer.getAddress());
console.log("Proposal:", value.proposal);
console.log("Nonce:", nonce.toString());
console.log("Signature:", signature);
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exitCode = 1;
});
记得将contractAddress更新为你已部署的合约地址。
7. 生成签名
运行签名脚本:
npx hardhat run scripts/sign.js --network eSpaceTestnet
将产生签名信息。
8. 创建投票脚本
创建一个scripts/vote.js文件:
const hre = require("hardhat");
async function main() {
const contractAddress = "<YOUR_DEPLOYED_CONTRACT_ADDRESS>";
const EIP712Voting = await hre.ethers.getContractFactory("EIP712Voting");
const contract = EIP712Voting.attach(contractAddress);
const proposal = 1; // Same as the proposal number used in the signature
const signature = "<YOUR_SIGNATURE>";
const tx = await contract.castVote(proposal, signature);
await tx.wait();
console.log("Vote cast successfully");
const voteCount = await contract.getVoteCount(proposal);
console.log("Vote count for proposal", proposal, ":", voteCount.toString());
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exitCode = 1;
});
用你的实际值更新contractAddress和signature。
9. 执行投票
运行投票脚本:
npx hardhat run scripts/vote.js --network eSpaceTestnet
这将使用生成的签名进行投票。
10. 创建前端界面
创建一个public/sign.html文件:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>EIP-712 Voting with MetaMask</title>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/ethers/6.7.0/ethers.min.js"></script>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
max-width: 800px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 20px;
}
button {
margin: 10px 0;
padding: 10px;
}
#status,
#result,
#voteInfo {
margin-top: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>EIP-712 Voting with MetaMask</h1>
<button id="connectButton">Connect MetaMask</button>
<div id="status"></div>
<div id="votingSection" style="display:none;">
<h2>Cast Your Vote</h2>
<input
type="number"
id="proposalInput"
placeholder="Enter proposal number"
/>
<button id="voteButton">Vote</button>
</div>
<div id="result"></div>
<div id="voteInfo"></div>
<script type="module">
import { ethers } from "https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/ethers/6.7.0/ethers.min.js";
const contractAddress = "YOUR_DEPLOYED_CONTRACT_ADDRESS";
const contractABI = [
"function nonces(address owner) view returns (uint256)",
"function castVote(uint256 proposal, bytes memory signature) external",
"function getVoteCount(uint256 proposal) view returns (uint256)",
"function getVoterProposal(address voter) view returns (uint256)", // Assuming this function exists in the contract
];
let provider, signer, contract;
const connectButton = document.getElementById("connectButton");
const statusDiv = document.getElementById("status");
const votingSection = document.getElementById("votingSection");
const proposalInput = document.getElementById("proposalInput");
const voteButton = document.getElementById("voteButton");
const resultDiv = document.getElementById("result");
const voteInfoDiv = document.getElementById("voteInfo");
const checkVoteButton = document.getElementById("checkVoteButton");
connectButton.addEventListener("click", async () => {
if (typeof window.ethereum !== "undefined") {
try {
await window.ethereum.request({ method: "eth_requestAccounts" });
provider = new ethers.BrowserProvider(window.ethereum);
signer = await provider.getSigner();
contract = new ethers.Contract(
contractAddress,
contractABI,
signer
);
const address = await signer.getAddress();
statusDiv.innerHTML = ``;
votingSection.style.display = "block";
checkVoteButton.style.display = "block";
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
statusDiv.innerHTML = "Failed to connect to MetaMask";
}
} else {
statusDiv.innerHTML = "Please install MetaMask";
}
});
voteButton.addEventListener("click", async () => {
const proposal = proposalInput.value;
if (!proposal) {
alert("Please enter a proposal number");
return;
}
try {
const address = await signer.getAddress();
const nonce = await contract.nonces(address);
const domain = {
name: "EIP712Voting",
version: "1",
chainId: Number((await provider.getNetwork()).chainId),
verifyingContract: contractAddress,
};
const types = {
Vote: [
{ name: "voter", type: "address" },
{ name: "proposal", type: "uint256" },
{ name: "nonce", type: "uint256" },
],
};
const value = {
voter: address,
proposal: BigInt(proposal),
nonce: nonce,
};
const signature = await signer.signTypedData(domain, types, value);
const tx = await contract.castVote(proposal, signature);
await tx.wait();
const voteCount = await contract.getVoteCount(proposal);
resultDiv.innerHTML = ``;
} catch (error) {
console.error("Voting error:", error);
let errorMessage = error.message;
if (error.data && typeof error.data.message === "string") {
const match = error.data.message.match(
/execution reverted: (.*?)(?:\.?$)/
);
if (match) {
errorMessage = match[1];
}
}
resultDiv.innerHTML = "Failed to cast vote: " + errorMessage;
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
这个 HTML 文件提供了一个简单的用户界面,用于连接 MetaMask、投票以及查看投票结果。
11. 运行前端
使用Live Server或其他HTTP服务器运行public/sign.html。 确保将contractAddress更新为你已部署的合约地址。
结论
通过本教程,你已经学习了如何使用 Hardhat 在 Conflux eSpace 上实现 EIP-712 签名。 这包括编写和部署智能合约、生成和验证签名,以及创建一个与合约交互的简单前端界面。
请记住,始终保护你的私钥,并在进行任何真实交易之前,在测试网上彻底测试你的应用程序。